Cooperative banks in India are financial institutions that operate on the principles of cooperation, mutual assistance, and democratic governance. They are established under the Cooperative Societies Act and regulated by both the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the respective State Cooperative Authorities. These banks primarily serve small businesses, farmers, and low-income groups, offering affordable banking and credit facilities to promote financial inclusion.
Numbers to Remember
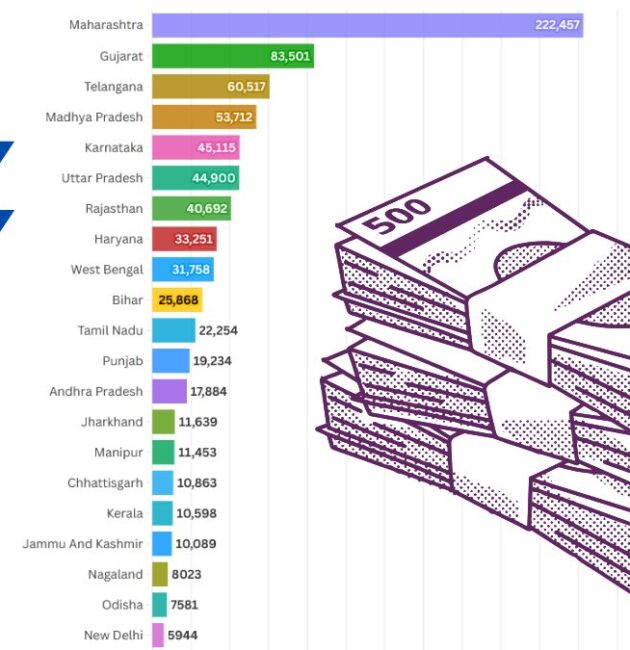
According to the data sourced from RBI and NABARD, the number of cooperative banks and cooperative societies in the country are as under:
Facts you must remember
Cooperative banking in India has a three-tier structure in rural areas, consisting of Primary Agricultural Credit Societies (PACS), District Cooperative Banks, and State Cooperative Banks, while Urban Cooperative Banks (UCBs) cater to city-based customers.
The cooperative banking sector plays a vital role in supporting agriculture, small-scale industries, and self-employment, contributing significantly to the rural economy.
Cooperative banks are inherently cooperative societies which are registered under the Cooperative Societies Act of the State concerned or under the Multi-State Cooperative Societies Act, 2002. When cooperative societies carry on the business of banking, they come under the regulatory purview of RBI and they are licensed under the provisions of the Banking Regulation Act, 1949 (as applicable to cooperative societies).
All the cooperative banks under the supervision of NABARD have been digitized and are functional on the Core Banking Solution (CBS) platform. Cooperative banks are a crucial part of India’s banking and financial system, strengthening inclusive growth and socio-economic development across the country.
Topic is Important for:
UPSC, SSC, Banking Services, India Post Jobs, State PCS, Subordinate Class, etc.