Palm trees are an integral part of Africa’s ecosystem and economy, providing numerous benefits to local communities. With over 60 million people depending on palm oil and other palm products for their livelihoods, these versatile trees have been a cornerstone of African life for centuries (FAO, 2020). Let’s discuss the world-wide scenario of Palm oil production, with focus on African Countries and India.
Indonesia Leads Global Palm Oil Production
As of 2025, Indonesia remains the world’s leading producer of palm oil, contributing approximately 46.5 million metric tons annually. This accounts for over half of global production, solidifying Indonesia’s position at the top of the palm oil industry.
Top Palm Oil-Producing Countries in Africa
Africa plays a growing role in global palm oil production, led by Nigeria, the continent’s top producer. According to Foreign Agricultural Services, United States latest report Ghana, Côte d’Ivoire, and Cameroon are the significant contributors. These countries utilize palm oil for domestic consumption and export, supporting local economies. However, challenges like outdated farming practices and sustainability concerns continue to impact production efficiency and environmental outcomes.
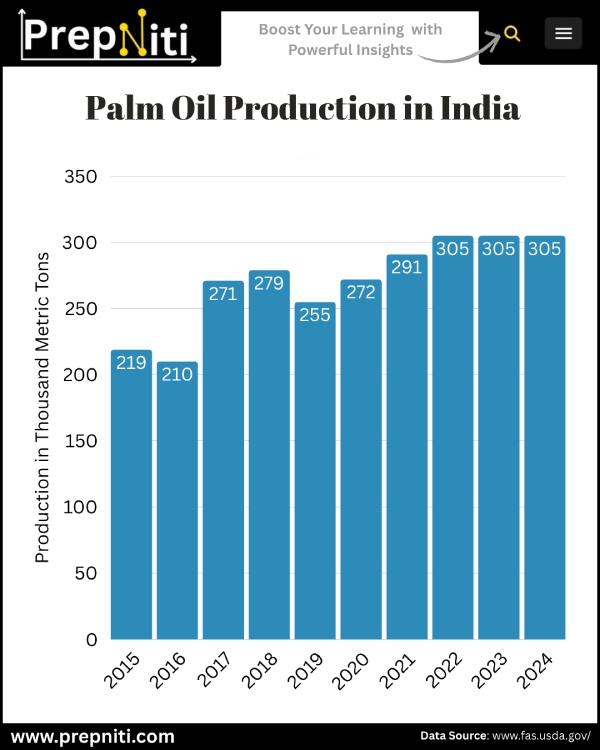
India’s Palm Oil Production Snapshot
- Global Rank: #13
- 10-Year Average Production (MY 2015–2024): 271,200 metric tons
- 10-Year Compound Average Growth: 3% (MY 2015–2024)
- Production in 2023/2024: 305,000 metric tons
- Projected Production for 2024/2025: 305,000 metric tons
- Year-over-Year Change: 0%
Drought Threatens Palms
Palm trees offer a wide range of uses that cater to the needs of the people, including:
- Nutrition: Palm fruits are a rich source of nutrition, with Africa producing over 3.5 million metric tons of palm oil annually (International Palm Oil Council, 2022).
- Employment: The palm oil industry provides employment opportunities for millions of people in Africa, with countries like Nigeria and Ghana relying heavily on palm oil production for income.
- Economic contribution: Palm oil and other palm products contribute significantly to local economies, generating billions of dollars in revenue each year.

However, palm trees are facing threats from logging activities, primarily carried out by African loggers, which poses a significant challenge to their long-term survival. The loss of palm trees can have far-reaching consequences, including:
- Soil erosion: Deforestation due to logging can lead to soil erosion, decreased biodiversity, and reduced economic opportunities.
- Biodiversity loss: Palm tree forests are home to a diverse range of species, and their destruction can lead to loss of habitat and extinction.
To mitigate the impact of logging and ensure the preservation of palm trees, several strategies can be employed:
- Responsible forestry practices: Implementing selective logging and reforestation can help maintain healthy palm tree populations.
- Community engagement: Educating local communities about the importance of preserving palm trees and involving them in conservation efforts can foster a sense of ownership and responsibility.
- Alternative livelihoods: Providing alternative sources of income for loggers and local communities can reduce reliance on palm tree logging.
- Protected areas: Establishing protected areas and national parks can safeguard palm tree populations and provide a safe haven for biodiversity.
Overall, palm trees are a vital part of Africa’s ecosystem and economy, and their preservation is essential for the well-being of local communities. By working together to implement sustainable forestry practices, engage local communities, provide alternative livelihoods, and establish protected areas, we can ensure the long-term sustainability of these valuable resources and support the well-being of local communities.
[ays_poll cat_id=3]




