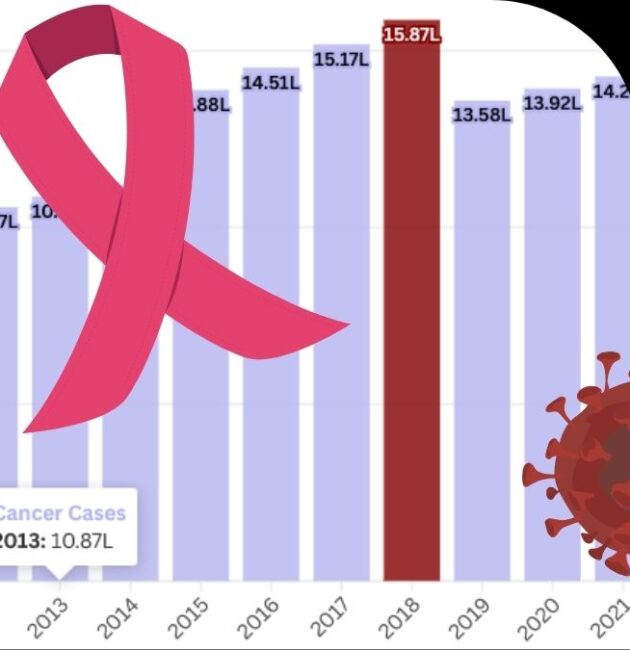
Cancer has emerged as a major public health challenge in India over the past decade, with a steady rise in the number of diagnosed cases. From 2010 to 2024, the country has witnessed a significant increase in cancer incidence, driven by factors such as lifestyle changes, environmental pollution, genetic predisposition, and improved diagnostic capabilities.
Currently, around 100 out of every 1 lakh people in India are diagnosed with cancer, highlighting its widespread impact. According to the Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR), the estimated number of cancer cases in India surpassed 14 lakh in 2023, reflecting the growing burden of the disease. Common cancers such as breast, lung, cervical, and oral cancers continue to affect millions, making early detection and effective treatment crucial.
Cancer Cases in India (2010-2024): Key Data
Key Highlights on Cancer Cases in India
Budget Allocation for FY 2025-26
- The Ministry of Health and Family Welfare has been allocated ₹99,858.56 crore.
- ₹95,957.87 crore is designated for the Department of Health and Family Welfare.
- ₹3,900.69 crore is allocated to the Department of Health Research.
Expansion of Day Care Cancer Centres
- The government plans to establish Day Care Cancer Centres in all district hospitals within the next three years.
- 200 centres are scheduled to be set up in FY 2025-26.
Customs Duty Exemptions to Reduce Cancer Treatment Costs
- 36 lifesaving drugs for cancer, rare diseases, and chronic illnesses are fully exempted from Basic Customs Duty (BCD).
- Six lifesaving medicines will attract a reduced 5% customs duty.
- Patient Assistance Programme drugs provided by pharmaceutical companies will be fully exempted from BCD.
Financial Aid for Cancer Patient
Health Minister’s Cancer Patient Fund (HMCPF)
- Under Rashtriya Arogya Nidhi (RAN), financial assistance of up to ₹5 lakh is available for cancer treatment for patients below the poverty line.
- The maximum assistance under the scheme is ₹15 lakh.Treatment is available at 27 Regional Cancer Centres (RCCs).
- ₹50 lakh revolving funds are allocated to each centre.
- Established in 2009, the scheme ensures affordable cancer care for underprivileged patients.
National Cancer Grid (NCG) – Strengthening Cancer Care
- Established in 2012, the National Cancer Grid (NCG) standardizes high-quality cancer care across India.
- It has grown into the world’s largest cancer network with 287 member institutions, including cancer centres, research bodies, and advocacy groups.
- The network treats over 750,000 new cancer patients annually, covering more than 60% of India’s cancer burden.
- NCG collaborates with Ayushman Bharat – PMJAY to provide affordable, evidence-based cancer treatment.
- It has played a crucial role in shaping the National Digital Health Mission (NDHM) through electronic patient health records.
National Programme for Prevention and Control of Cancer, Diabetes, Cardiovascular Diseases, and Stroke (NPCDCS)
NPCDCS is a flagship initiative under the National Health Mission (NHM) aimed at controlling non-communicable diseases (NCDs), including cancer. The program prioritizes oral, breast, and cervical cancers through prevention, early detection, and enhanced treatment infrastructure.
Key Components of NPCDCS
- Cancer Screening: Community-level screening for oral, breast, and cervical cancers.
- Early Detection & Awareness: Utilizing health workers and digital platforms for awareness.
- Strengthening Infrastructure: Establishment of Tertiary Cancer Centres (TCCs) and State Cancer Institutes (SCIs).
Infrastructure Strengthening Under NPCDCS:
- 770 District NCD Clinics
- 233 Cardiac Care Units
- 372 District Day Care Centres
- 6,410 Community Health Centre NCD Clinics
These facilities ensure accessible and affordable cancer screenings, particularly for oral, breast, and cervical cancers.
Topic “Cancer Awareness” is Important for:
Key exams where cancer awareness, healthcare policies, and disease control programs are crucial – UPSC Combined Medical Services (CMS) Exam, NEET-PG & INI-CET, ESIC (Employees’ State Insurance Corporation) Exams, NHM (National Health Mission) Exams, State Health Department Exams, Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) JRF & Scientist Recruitment, FSSAI (Food Safety and Standards Authority of India) Exams, Exams for Health Officers under state PSC, etc.